Introduction
- Electronic waste (e-waste) has emerged as a significant environmental and public health concern in recent decades due to the rapid proliferation of electronic devices and their relatively short lifecycle. E-waste encompasses a wide range of discarded electrical or electronic devices, including computers, smartphones, televisions, and household appliances. Improper handling and disposal of e-waste can lead to environmental pollution, resource depletion, and health hazards from toxic substances such as lead, mercury, and cadmium.
- Efficient management of e-waste is essential to mitigate its adverse impacts on the environment and human health. This involves implementing strategies for the proper collection, recycling, and disposal of electronic devices at the end of their lifecycle. Additionally, promoting awareness and responsible consumption practices among consumers and industry stakeholders is crucial for reducing the generation of e-waste and encouraging sustainable product design and manufacturing.
- In the context of technological advancements, Arduino, an open-source electronics platform, offers opportunities to address challenges associated with e-waste management. Arduino-based projects can range from monitoring and controlling e-waste recycling processes to developing innovative solutions for sorting and repurposing electronic components. By leveraging sensors, actuators, and data processing capabilities, Arduino projects contribute to enhancing the efficiency, safety, and sustainability of e-waste management practices.
- In this context, we explore a basic Arduino project aimed at monitoring and controlling an e-waste recycling process. This project exemplifies how Arduino technology can be utilized to address specific challenges in e-waste management while fostering environmental stewardship and sustainable development.
Projects Categories:
Products Categories:
- Robotics
- Actuators
- Camera Modules
- Drone Kits
- Drone Components
- Chassis
- DC Motors
- Other Robotic accessories
- Pick and Place Modules
- Robotic Kit
- Servo Motors
- Stepper Motors
- Wheels
- Microcontrollers & Programmers
- 8051 Microcontroller
- Arduino Microcontroller
- ARM Development Board
- Interface Module
- NODMCU / ESP Modules
- PIC Microcontroller
- Raspberry Pi
- Devices and Actuators
- Display Modules
- Sensors & Module
- Power Supply / Batteries
- Wireless modules
- Electronic Components
- Wholesale Market
Description
- Electronic waste (e-waste) management is a complex and multifaceted challenge that requires innovative solutions to ensure environmental sustainability and public health protection. Arduino, an open-source electronics platform, plays a crucial role in addressing various aspects of e-waste management due to its versatility, accessibility, and affordability. Here are some reasons why Arduino is important in e-waste management:
1. Monitoring and Control Arduino
- enables the development of monitoring and control systems for e-waste recycling processes. By integrating sensors to measure parameters such as temperature, humidity, and gas emissions, Arduino-based systems can monitor the efficiency and safety of recycling operations. Additionally, Arduino can control actuators to automate processes and ensure optimal resource utilization.
2. Data Collection and Analysis
- Arduino facilitates the collection, processing, and analysis of data related to e-waste management. Sensor data can be logged, transmitted wirelessly, or stored locally for further analysis. This data-driven approach enables informed decision-making, optimization of recycling processes, and identification of trends and patterns for continuous improvement.
3. Education and Awareness
- Arduino serves as a valuable educational tool for raising awareness about e-waste management among students, educators, and the general public. Arduino-based projects provide hands-on learning experiences, allowing individuals to understand the environmental impacts of e-waste and explore sustainable solutions. By promoting STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) education, Arduino empowers future generations to become responsible stewards of the environment.
4. Innovation and Prototyping
- Arduino fosters innovation and prototyping of new technologies and solutions for e-waste management. Entrepreneurs, researchers, and community organizations can leverage Arduino to develop novel approaches for e-waste collection, recycling, and reuse. Rapid prototyping with Arduino enables iterative design iterations, quick validation of concepts, and scalability of solutions to address diverse e-waste challenges.
5. Accessibility and Affordability
- Arduino’s open-source nature and low-cost hardware make it accessible to a wide range of users, including individuals in developing countries and underserved communities. This democratization of technology empowers grassroots initiatives and local entrepreneurs to implement sustainable e-waste management practices tailored to their specific needs and resources.
- In summary, Arduino plays a significant role in e-waste management by enabling the development of monitoring systems, data-driven decision-making, educational initiatives, innovation, and inclusive solutions. By leveraging Arduino technology, stakeholders can collaborate to address the growing e-waste crisis and promote a circular economy where electronic products are recycled, refurbished, and repurposed to minimize environmental impact and maximize resource efficiency.
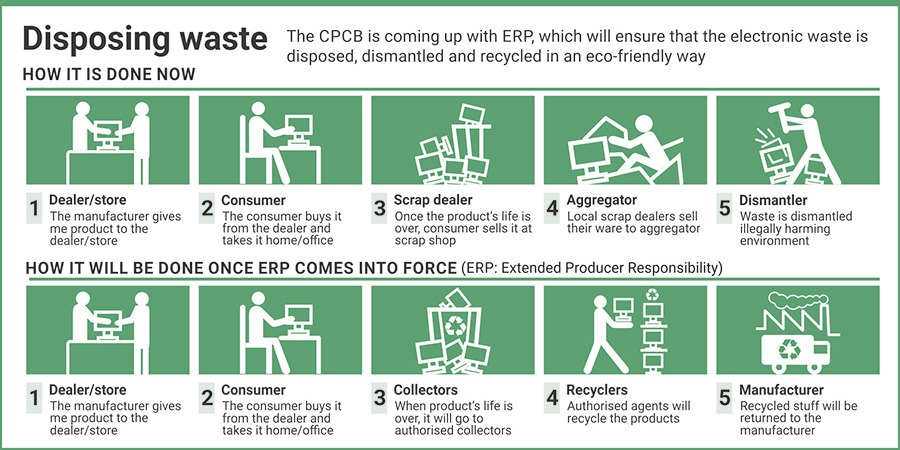
E Waste Management Developments
- Several countries around the world are making significant strides in e-waste management, implementing policies, regulations, and initiatives to address the challenges posed by electronic waste. While it’s difficult to pinpoint a single country as the sole leader in e-waste management, several nations stand out for their efforts and achievements in this field:
1. Germany
- Germany is often recognized for its advanced waste management infrastructure and stringent regulations regarding e-waste recycling. The country has established extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes, which require manufacturers to take financial responsibility for the collection, recycling, and disposal of their products. Germany also boasts high rates of e-waste recycling and recovery.
2. Switzerland
- Switzerland is known for its innovative approach to e-waste management and circular economy principles. The country has implemented comprehensive e-waste collection and recycling programs, with high rates of collection and recycling of electronic devices. Switzerland also promotes eco-design and sustainable product development to minimize e-waste generation.
3. Japan
Japan has a well-developed e-waste recycling infrastructure and strict regulations governing the disposal of electronic devices. The country has implemented advanced recycling technologies to recover valuable materials from e-waste, such as rare earth metals, precious metals, and plastics. Japan also encourages collaboration between industry stakeholders to promote sustainable e-waste management practices.
4. South Korea
- South Korea has made significant investments in e-waste recycling facilities and technologies to handle the growing volume of electronic waste. The government has introduced policies to promote the recycling of electronic devices and discourage illegal dumping. South Korea also emphasizes public awareness and education campaigns to encourage responsible e-waste disposal among citizens.
5. Netherlands
- The Netherlands has implemented effective e-waste collection and recycling programs, supported by government initiatives and private sector partnerships. The country has established collection points for electronic devices and incentivizes citizens to recycle their e-waste through deposit refund systems and take-back programs. The Netherlands also promotes research and innovation in e-waste recycling technologies.
6. Norway
- Norway has prioritized e-waste management as part of its broader environmental sustainability goals. The country has implemented comprehensive legislation to regulate the collection, treatment, and recycling of electronic waste. Norway also supports initiatives to promote circular economy principles and sustainable consumption practices.
- These countries serve as examples of best practices in e-waste management, demonstrating the importance of collaboration between government, industry, academia, and civil society to address the challenges posed by electronic waste effectively. By adopting holistic approaches and embracing innovation, these nations are leading the way towards a more sustainable and circular economy.
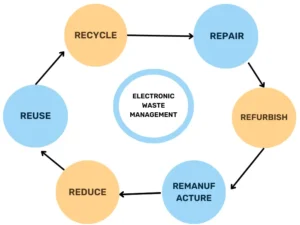
E Waste Management types
E-waste management encompasses various strategies and approaches aimed at handling electronic waste in an environmentally sustainable and socially responsible manner. Here are some types of e-waste management:
1. Collection and Transport
This involves the collection, sorting, and transportation of electronic waste from households, businesses, and other sources to designated e-waste recycling facilities or disposal sites. Proper collection and transport are essential to ensure that e-waste is handled safely and efficiently.
2. Recycling and Recovery
Recycling and recovery are key components of e-waste management, aimed at recovering valuable materials from discarded electronic devices. Recycling processes involve disassembling, shredding, and sorting e-waste into various components such as metals, plastics, and glass. These materials can then be processed and recycled into new products or used as raw materials in manufacturing processes. Recovery also includes the extraction of precious metals and other valuable resources from electronic waste through specialized technologies and techniques.
3. Refurbishment and Reuse
Refurbishment and reuse involve extending the lifespan of electronic devices by repairing, refurbishing, or upgrading them for resale or donation. This approach helps to reduce e-waste generation by giving old devices a second life and promoting the circular economy. Refurbished electronics undergo thorough testing and quality assurance processes to ensure they meet safety and performance standards before being reintroduced into the market.
4. Disposal and Treatment
Disposal and treatment refer to the proper disposal of electronic waste that cannot be recycled, reused, or refurbished. This may involve environmentally sound methods such as landfilling, incineration, or specialized treatment processes for hazardous components. Proper disposal and treatment are essential to prevent environmental pollution, contamination of soil and water, and health risks associated with toxic substances found in e-waste.
5. Policy and Regulation
Policy and regulation play a crucial role in e-waste management by establishing legal frameworks, standards, and guidelines for the handling, recycling, and disposal of electronic waste. Governments enact laws and regulations to ensure the proper management of e-waste, promote producer responsibility, and enforce compliance with environmental and safety standards. Effective policy measures include extended producer responsibility (EPR) schemes, waste electrical and electronic equipment (WEEE) directives, and bans on the export of hazardous e-waste to developing countries.
6. Awareness and Education
Awareness raising and education initiatives are essential for promoting responsible e-waste disposal practices among consumers, businesses, and other stakeholders. These efforts aim to increase public awareness about the environmental and health impacts of e-waste, encourage recycling and reuse behaviors, and provide information on available e-waste management options and resources. Awareness campaigns, educational programs, and community outreach activities help to foster a culture of sustainability and environmental stewardship.
By employing a combination of these e-waste management strategies and approaches, stakeholders can work together to minimize the environmental footprint of electronic waste and promote sustainable consumption and production patterns.
Conclusion
In conclusion, e-waste management is a critical aspect of environmental sustainability and public health, necessitating comprehensive strategies and collaboration among various stakeholders. By implementing effective collection, recycling, refurbishment, disposal, policy, and awareness initiatives, we can address the challenges posed by electronic waste and promote a circular economy where resources are conserved and waste is minimized.
In the real world e-waste management has several uses and applications
1. Resource Recovery
Recycling e-waste allows for the recovery of valuable materials such as metals, plastics, and glass, which can be reused in manufacturing processes. This conserves natural resources and reduces the need for virgin materials, contributing to resource efficiency and cost savings.
2. Environmental Protection
Proper e-waste management helps prevent environmental pollution and ecosystem degradation caused by the improper disposal of electronic waste. By recycling and treating e-waste, we can minimize the release of hazardous substances into the environment, safeguarding soil, water, and air quality.
3. Health Promotion
- Responsible e-waste management protects public health by reducing exposure to toxic substances found in electronic devices, such as lead, mercury, and brominated flame retardants. By minimizing the risks associated with e-waste, we can mitigate health problems such as respiratory diseases, neurological disorders, and reproductive issues.
4 .Job Creation
- The e-waste recycling industry creates employment opportunities in collection, sorting, recycling, and refurbishment activities. By investing in e-waste management infrastructure and capacity building, countries can stimulate economic growth, generate income, and support livelihoods in local communities.
5. Technology Innovation
- E-waste management drives innovation in recycling technologies, materials science, and waste reduction strategies. Researchers and entrepreneurs develop new methods and solutions for recycling electronic waste, recovering valuable resources, and minimizing environmental impact. These innovations contribute to technological advancements and the development of sustainable practices in the electronics industry.
6. Regulatory Compliance
- Governments enact policies, regulations, and standards to regulate the handling, recycling, and disposal of electronic waste. Compliance with these legal requirements ensures the responsible management of e-waste and holds producers accountable for their products’ end-of-life management. This fosters transparency, accountability, and environmental responsibility within the electronics industry.
- In summary, e-waste management has significant uses and applications in the real world, ranging from resource recovery and environmental protection to health promotion, job creation, technology innovation, and regulatory compliance. By embracing sustainable e-waste management practices, we can build a more resilient and equitable society that prioritizes environmental stewardship and human well-being.
For additional blog content, to explore further insights and articles. Click here
How to attach heat sink
How to attach heat sink to raspberry pi 4 INTRODUCTION Attaching a heat sink to...
Read MoreUnderstanding Integrated Circuit And Microchips
Understanding Integrated Circuit And Microchips Introduction Integrated circuits (ICs), often referred to as microchips, are...
Read MoreExploring The world of Quantum
Exploring The World Of Quantum Sensors Quantum sensors are fascinating devices that leverage the principles...
Read MoreRaspberry Pi Microcontroller
Raspberry Pi Introduction Welcome to the world of Raspberry Pi projects, where creativity meets technology!...
Read More