Introduction
- The COVID-19 pandemic has had a significant impact on the electronics industry, both positively and negatively.
- The COVID-19 pandemic has reshaped industries worldwide, and the electronics sector is no exception. This unprecedented global health crisis has led to significant shifts in consumer behavior, disrupted supply chains, and accelerated digital transformation. From increased demand for remote work and learning tools to challenges in manufacturing and supply chain logistics, the impact of COVID-19 on the electronics industry is multifaceted and far-reaching. In this discussion, we’ll explore the various ways in which the pandemic has influenced the electronics sector, both positively and negatively, and the implications for manufacturers, consumers, and the broader economy.
Projects Categories:
Products Categories:
- Robotics
- Actuators
- Camera Modules
- Drone Kits
- Drone Components
- Chassis
- DC Motors
- Other Robotic accessories
- Pick and Place Modules
- Robotic Kit
- Servo Motors
- Stepper Motors
- Wheels
- Microcontrollers & Programmers
- 8051 Microcontroller
- Arduino Microcontroller
- ARM Development Board
- Interface Module
- NODMCU / ESP Modules
- PIC Microcontroller
- Raspberry Pi
- Devices and Actuators
- Display Modules
- Sensors & Module
- Power Supply / Batteries
- Wireless modules
- Electronic Components
- Wholesale Market
Description
- The COVID-19 pandemic has presented both challenges and opportunities for the electronics industry. Initially, as lockdowns and social distancing measures were implemented worldwide, there was a surge in demand for electronics that facilitate remote work, learning, and entertainment. Products like laptops, tablets, webcams, and monitors experienced increased sales as people adapted to new ways of living and working. However, alongside this spike in demand came disruptions to the global supply chain. Factories closures, transportation restrictions, and component shortages led to production delays and supply chain bottlenecks, impacting manufacturers and consumers alike.
- Moreover, the shift towards remote work arrangements posed additional challenges for electronics manufacturers. Adapting manufacturing processes to comply with health and safety guidelines required significant adjustments, increasing operational costs and, in some cases, reducing production capacity. Despite these challenges, the pandemic also accelerated the digital transformation of industries. Investments in technologies such as cloud computing, IoT, and AI surged as businesses sought to adapt to the new normal. This created opportunities for electronics manufacturers to innovate and develop new products and solutions to support this digital shift.
- However, amidst this uncertainty, market volatility remained a constant concern. Fluctuations in consumer demand, supply chain disruptions, and geopolitical tensions contributed to market instability, posing challenges for manufacturers and investors alike. Yet, the resilience of the electronics industry has been evident as companies adapted to the evolving landscape. Whether through diversifying supply chains, investing in automation, or developing new business models, electronics manufacturers have demonstrated their ability to navigate the challenges brought about by the pandemic.
Effects From Covid 19 to Pcb Industries
1. Supply Chain Disruptions
- The global PCB assembly industry heavily relies on a complex network of suppliers, many of whom were affected by lockdowns, travel restrictions, and disruptions to manufacturing operations. This led to delays in the procurement of essential components, such as integrated circuits, resistors, and capacitors, impacting production schedules and leading to potential bottlenecks in PCB assembly.
2. Production Delays and Cancellations
- Many PCB assembly facilities faced temporary closures or reduced operating capacities due to government-imposed lockdowns and social distancing measures. This resulted in production delays and cancellations, as manufacturers struggled to maintain workforce safety while meeting customer demands.
3. Remote Work Challenges
- The shift towards remote work arrangements posed logistical challenges for PCB assembly companies, particularly those reliant on on-site operations and manual assembly processes. Implementing remote work policies and ensuring employee safety protocols became critical priorities, impacting productivity and operational efficiency.
4. Increased Demand for Certain Applications
- On the other hand, certain segments of the PCB assembly industry experienced increased demand due to shifts in consumer behavior and market trends. For example, the demand for PCBs used in telecommunications infrastructure, medical devices, and consumer electronics surged as remote work, telemedicine, and online entertainment became more prevalent during the pandemic.
5. Adoption of Automation and Digital Solutions
- To mitigate the impact of COVID-19 on production capabilities and workforce limitations, many PCB assembly companies accelerated their adoption of automation and digital solutions. Robotic assembly systems, AI-driven quality control, and remote monitoring technologies were implemented to improve efficiency, reduce labor dependency, and ensure continuity of operations.
6. Supply Chain Diversification
- In response to the vulnerabilities exposed by the pandemic, some PCB assembly companies have begun diversifying their supply chains to reduce reliance on single-source suppliers and mitigate future risks. This includes exploring alternative sourcing options, regionalizing supply chains, and strengthening relationships with trusted suppliers.
7. Shift Towards Resilient Manufacturing
- The pandemic highlighted the importance of resilience and agility in manufacturing operations. PCB assembly companies have been investing in strategies and technologies that enhance their ability to adapt to unforeseen disruptions, such as flexible manufacturing processes, just-in-time inventory management, and remote monitoring capabilities.
- In summary, the COVID-19 pandemic has significantly impacted the PCB assembly industry, causing disruptions to supply chains, production processes, and workforce management. While challenges persist, the industry has also seen opportunities for innovation, resilience, and adaptation as companies seek to navigate the evolving landscape and emerge stronger from the crisis.
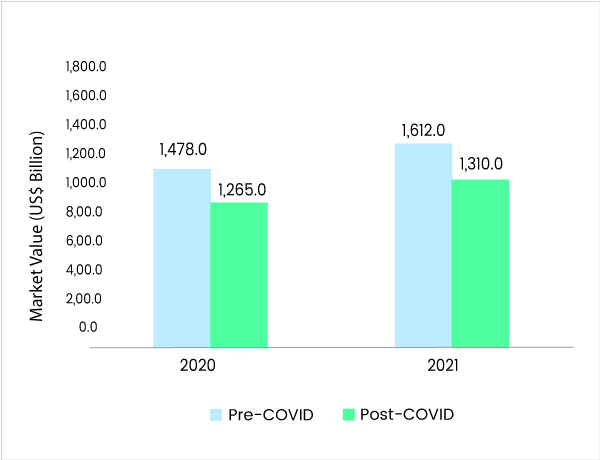
After Covid 19 Effects changes in The Electronics Industries
- Some changes in the electronics industry after COVID-19
- Rise of Telemedicine and Remote Healthcare Solutions The pandemic accelerated the adoption of telemedicine and remote healthcare solutions, driving demand for medical devices, wearables, and digital health technologies. Electronics companies responded by developing innovative solutions such as remote monitoring devices, telehealth platforms, and AI-powered diagnostic tools to support virtual healthcare delivery and patient care.
- Supply Chain Resilience and Localization The disruptions caused by COVID-19 highlighted the vulnerabilities of global supply chains in the electronics industry. As a result, there has been a shift towards building more resilient and localized supply chains, with companies diversifying sourcing strategies, reshoring manufacturing operations, and investing in domestic production capabilities to mitigate future risks and ensure supply chain stability.
- Focus on Health and Safety Technologies The pandemic prompted increased investment in technologies aimed at promoting health, safety, and sanitation. This includes the development of touchless interfaces, biometric authentication systems, thermal imaging cameras, and UV disinfection devices to reduce the risk of virus transmission in public spaces, workplaces, and commercial establishments.
- E-commerce Dominance and Omnichannel Strategies With physical retail outlets facing closures and restrictions, there was a significant shift towards online shopping and e-commerce channels for purchasing electronics products. Electronics companies adapted by expanding their online presence, enhancing e-commerce platforms, and implementing omnichannel strategies to meet changing consumer preferences and capitalize on the growing digital retail market.
- Environmental Sustainability and Green Technologies The pandemic underscored the importance of environmental sustainability and resilience in the electronics industry. Companies have increasingly focused on developing eco-friendly products, reducing carbon footprints, and adopting circular economy principles to minimize waste and promote resource efficiency. This includes the use of renewable materials, energy-efficient designs, and sustainable manufacturing practices to align with evolving environmental regulations and consumer preferences.
In Conclusion
- the COVID-19 pandemic has spurred significant transformations in the electronics industry, driving changes in consumer behavior, technological innovation, and business practices. From the increased emphasis on remote connectivity and digital transformation to the rise of telemedicine and supply chain resilience, the industry has adapted to meet the challenges and opportunities presented by the pandemic. As the world continues to navigate the post-pandemic landscape, the electronics industry remains at the forefront of innovation, shaping the future of connected technologies and driving sustainable growth in the digital economy. Embracing agility, resilience, and innovation will be essential for electronics companies to thrive in the evolving landscape and meet the evolving needs of consumers and society.
For additional blog content, to explore further insights and articles. Click here
How to attach heat sink
How to attach heat sink to raspberry pi 4 INTRODUCTION Attaching a heat sink to...
Read MoreUnderstanding Integrated Circuit And Microchips
Understanding Integrated Circuit And Microchips Introduction Integrated circuits (ICs), often referred to as microchips, are...
Read MoreExploring The world of Quantum
Exploring The World Of Quantum Sensors Quantum sensors are fascinating devices that leverage the principles...
Read MoreRaspberry Pi Microcontroller
Raspberry Pi Introduction Welcome to the world of Raspberry Pi projects, where creativity meets technology!...
Read More