Digital vs. Analog Electronics: Understanding the Difference
Introduction:
In the vast realm of electronics, two fundamental categories dominate the landscape: digital and analog. These two types of electronic systems serve as the foundation for countless devices and technologies we encounter in our daily lives. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of digital and analog electronics, exploring their characteristics, differences, and real-world applications.
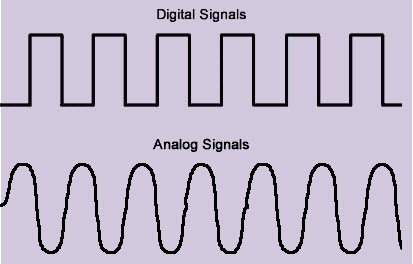

Digital Electronics:
Digital electronics process information using discrete, distinct signals represented by binary code—1s and 0s. This binary language forms the basis of all digital communication and computation. Key characteristics of digital electronics include:
Precision and Accuracy: Digital systems offer precise and accurate representation of data, as information is stored in a well-defined binary format.
Ease of Storage and Processing: Digital signals are conducive to storage and processing using electronic devices, making them suitable for complex calculations and data manipulation.
Robustness: Digital signals are less susceptible to noise and interference, ensuring reliable transmission and reception of information.
Flexible Design: Digital systems allow for easy modification and upgrading of hardware and software components, providing flexibility in design and implementation.


Analog Electronics:
Analog electronics, on the other hand, deals with continuous signals that vary smoothly over time. These signals can take an infinite number of values within a given range. Key characteristics of analog electronics include:
Smooth Signal Representation: Analog signals provide a continuous representation of information, allowing for smooth transitions between different values.
Real-world Accuracy: Analog systems are well-suited for tasks that require real-world accuracy, such as audio and video processing.
Complex Signal Processing: Analog electronics excel in tasks that involve complex signal processing, like amplification and filtering.
Limited Precision: Analog signals may suffer from signal degradation over long distances and are more susceptible to noise.